Introduction
When it comes to plumbing and piping systems, it’s important to choose the right materials for the job. Two commonly used materials in these systems are Schedule 80 CPVC and Schedule 80 PVC. While they may sound similar, there are significant differences between them that can impact their performance and suitability for specific applications. In this article, we will explore the differences between them to help you make an informed decision.
Schedule 80 CPVC
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride, is a thermoplastic piping material that is known for its durability and resistance to high temperatures and corrosive chemicals. CPVC pipes are made by chlorinating PVC resin, which enhances its heat resistance and chemical properties. Schedule 80 CPVC pipes are designed to handle higher pressure applications compared to Schedule 40 CPVC pipes.
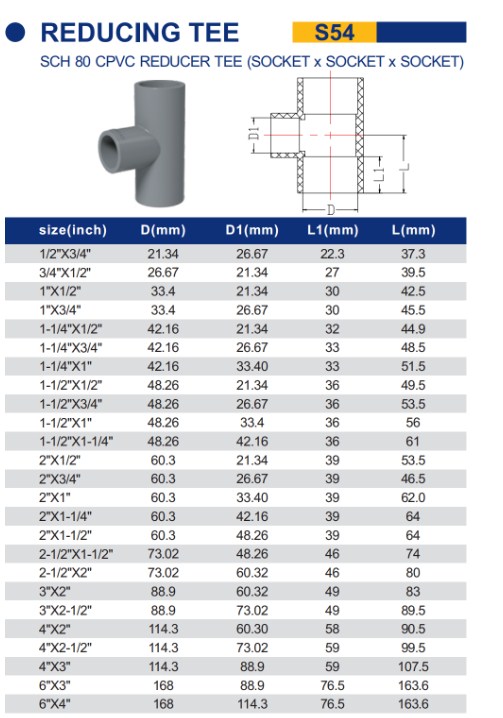
Schedule 80 PVC
Schedule 80 PVC, or Polyvinyl Chloride, is another commonly used material in plumbing and piping systems. PVC pipes are made from a combination of vinyl chloride monomers and various additives to enhance their strength and durability. Schedule 80 PVC pipes are thicker and stronger than Schedule 40 PVC pipes, making them suitable for applications that require higher pressure handling capabilities.
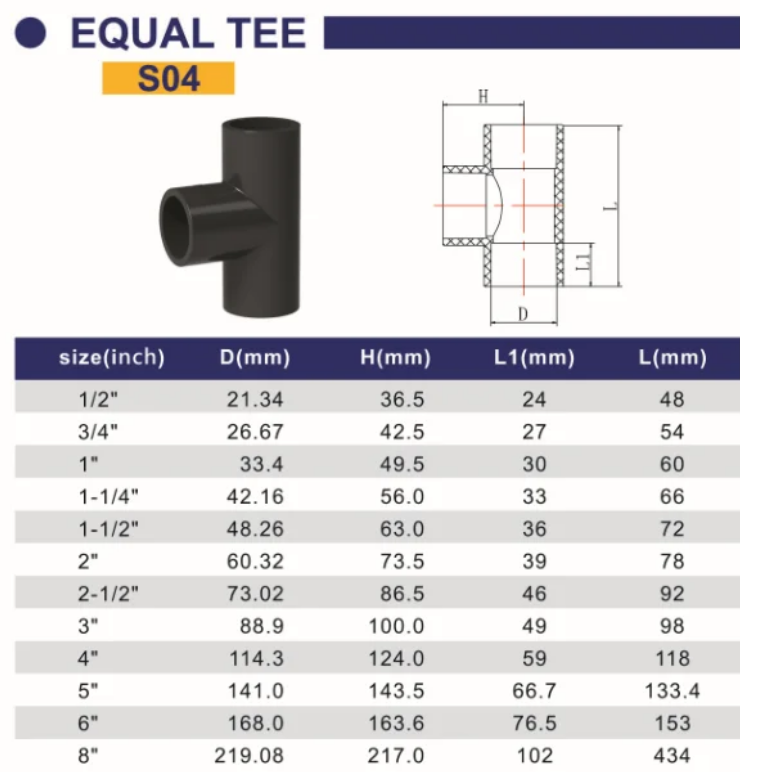
Differences between Schedule 80 CPVC and Schedule 80 PVC
1. Material Composition: The primary difference between them lies in their material composition. CPVC is PVC that has been chlorinated, which gives it enhanced heat resistance and chemical resistance compared to regular PVC.
2. Temperature Resistance: Schedule 80 CPVC has a higher temperature resistance than Schedule 80 PVC. CPVC can handle temperatures up to 200°F (93°C), while PVC is limited to temperatures up to 140°F (60°C). This makes CPVC a better choice for applications that involve hot water or high-temperature fluids.
3. Chemical Resistance: CPVC is highly resistant to a wide range of corrosive chemicals, including acids, bases, and salts. PVC, on the other hand, has good resistance to most non-oxidizing acids but may be susceptible to certain solvents and oxidizing agents. If your application involves handling corrosive chemicals, CPVC is the better choice.
4. Pressure Rating: Both of their pipes are designed to handle higher pressure applications compared to their Schedule 40 counterparts. However, CPVC pipes have a higher pressure rating than PVC pipes, making them suitable for applications that require higher pressure handling capabilities.
Applications
The choice between them will depend on the specific requirements of your plumbing or piping system. Here are some common applications for each:
Schedule 80 CPVC: hot and cold water distribution systems, industrial chemical handling, fire sprinkler systems, and underground piping.
Schedule 80 PVC: water supply lines, irrigation systems, drainage systems, and HVAC systems.

Conclusion
Both Schedule 80 CPVC and Schedule 80 PVC have their own unique properties and advantages. While CPVC offers enhanced temperature and chemical resistance, PVC is more cost-effective and suitable for general plumbing applications. Understanding the differences between these materials will help you make an informed decision when choosing the right material for your plumbing or piping system.
It is always recommended to consult with a professional plumber or piping expert to ensure you select the most appropriate material for your specific needs.



Leave A Comment